Rubber sheet
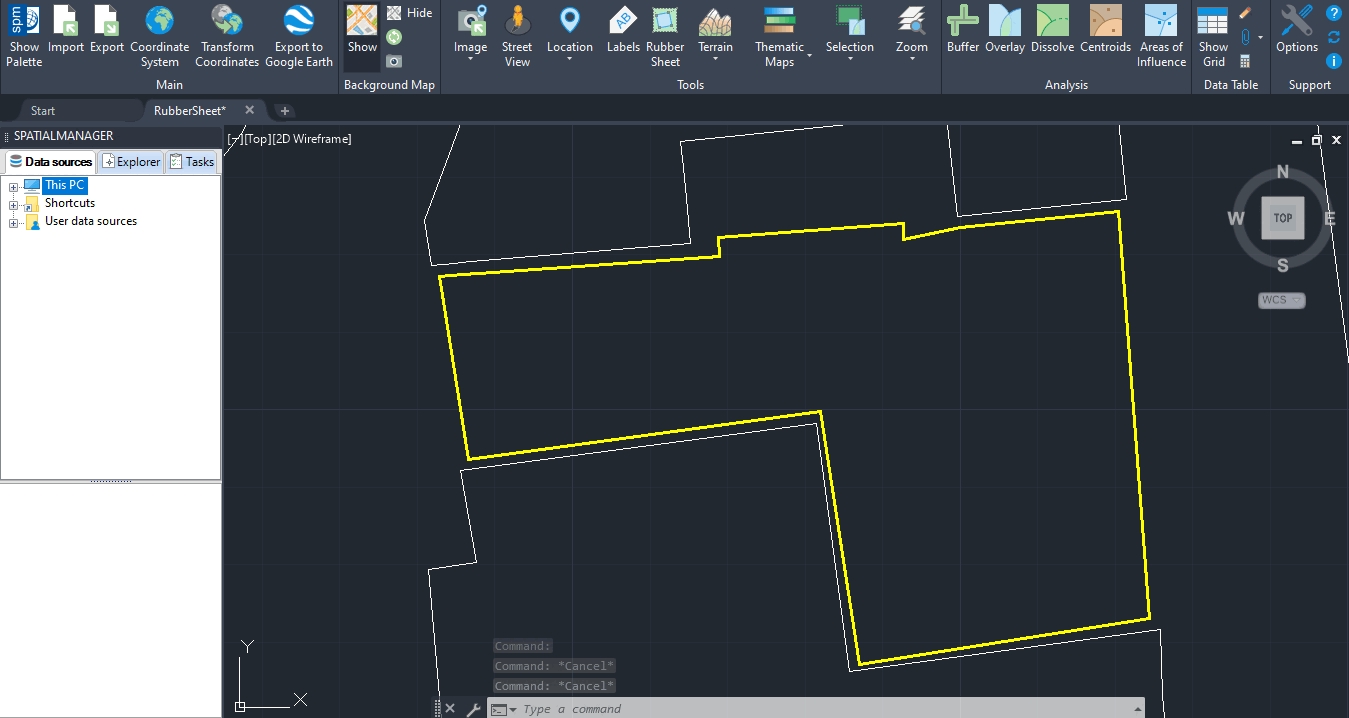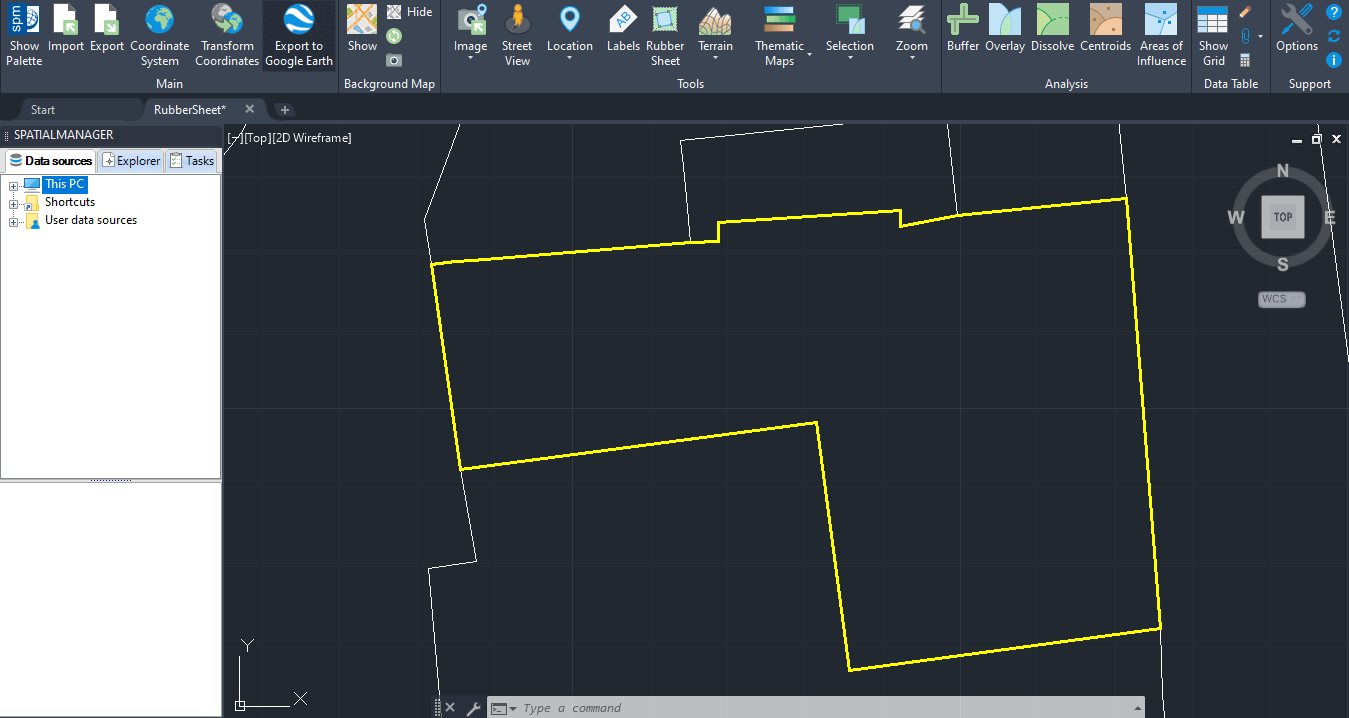
Geographically align two or more graphic datasets by defining control points that match known coordinates between them. This process adjusts the geometry of one dataset to fit another, correcting positional inaccuracies and improving spatial consistency across different data sources. It is especially useful when integrating legacy drawings, scanned maps, or misaligned layers into a unified coordinate framework..
Transform entities in order to geographically align them based on reference points
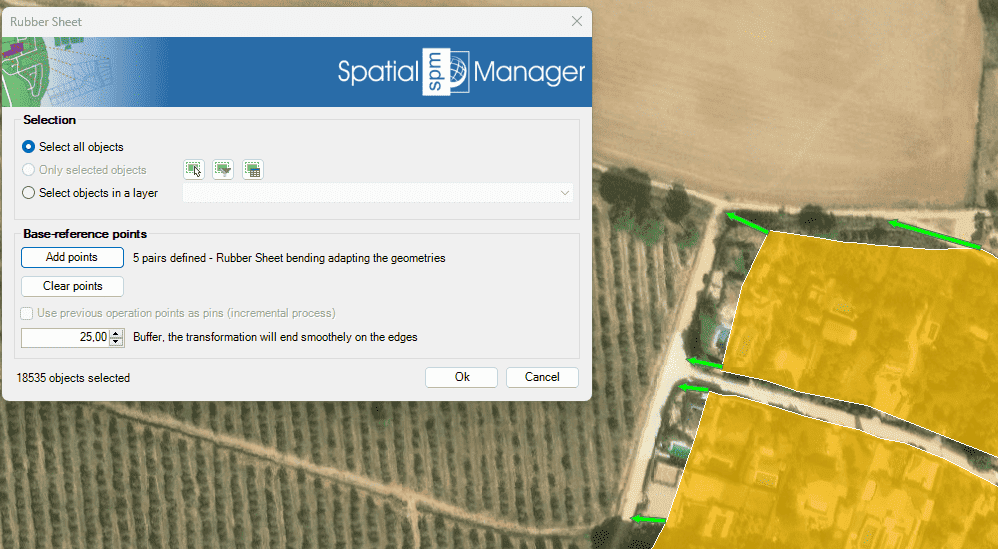
You can use the ‘SPMRUBBERSHEET’ command of Spatial Manager™ for BricsCAD to elastically deform (Rubber sheet) a set of selected entities by defining a set of source points and the equivalent set of target points.
For example, you can use this command when stretching a new subdivision map into a preexisting parcel map.
In the window of this command you can:
- Select the entities to deform (review selection control options).
- Base-reference points.
- Add points: You can add as many pairs of source/target points as you want (at least one pair) to define the desired transformation. The transformation method will vary depending on the number of base-reference points used.
- 1 pair of points: Translation, a simple offset according to the pair of points.
- 2 pairs of points: Translation, uniform scaling and rotation over the two pairs of points.
- 3 pairs of points: Affine transformation for matching.
- 4 or more pairs of points: Rubber Sheet bending, adapting the geometries (recommended).
- Clear points: Eliminates any previously defined pair of points.
- Use previous operation points as pins: Allows keeping previously defined points anchored in a transformation, which allows reaching the required result through several transformations incrementally.
- Add points: You can add as many pairs of source/target points as you want (at least one pair) to define the desired transformation. The transformation method will vary depending on the number of base-reference points used.
- Buffer.
- You can define a buffer width so that the calculations of the sides of the entities are better adjusted and without loss of precision or addition of superfluous vertices.
Note: For raster images, only up to two pairs of points can be used, so the transformation will be limited to translation, uniform scaling and rotation. Undesired results may occur if more base points are selected.
Disclaimer:
- Some components shown here (providers, names, window styles, etc.) may differ slightly from those on your computer.
- Certain features require Internet access. If you experience issues, check with your network administrator about a possible Proxy server. You can configure the Proxy settings in the application options.
- Some geographic data providers (Geocode, image maps, etc.) may require a user account, which you can set up in the Service Provider API Keys section of the application options.