Export spatial data
Export objects from BricsCAD to spatial files or databases, and saves their Extended Entity Data (EED) as alphanumeric data tables.
Export BricsCAD entities as spatial features
You can export BricsCAD entities as spatial features into files or databases by executing the SPMEXPORT command of Spatial Manager™ for BricsCAD, which you will find in the “Spatial Manager” BricsCAD ribbon. This will launch the “Export” wizard of the application, which shares some of the steps with the Import wizard. The command not only exports the selected entities but saves their Extended Entity Data (EED) as data tables (see below). Upon completion of any export process to a file, you can directly open the file location. When exporting to a KML or KMZ file you can choose to open the file in Google Earth (if installed).
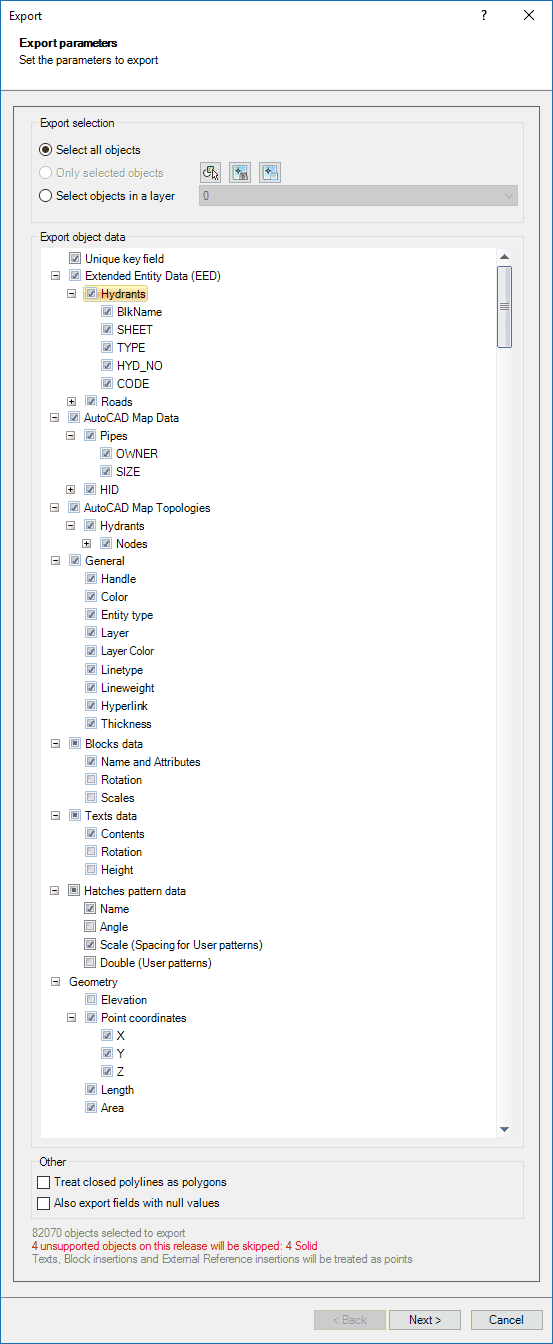
While running the “Export” wizard, you can select the export parameters that match your needs:
- Export selection (review selection control options).
- Export entity data (options tree).
- Unique key field: when checked, the data table will include a new Unique Key Field (numerical consecutive) (‘AdSPMKey’). This field will be defined as Primary Key if the target data provider uses keys (SQL Server Spatial, PostGIS, SQLite, etc.).
- Extended Entity Data (EED): the exported data table will include the entities data (Extended Entity Data (EED)). You can choose which tables and/or fields will be exported.
- BricsCAD Map Data and BricsCAD Map Topologies: if there are BricsCAD Map Entity Data or Topologies tables defined in the drawing, the exported data table will include this data. You can choose which Entity Data/Topologies tables and/or fields will be exported.
- General: when checked, the data table will include new fields for the corresponding BricsCAD entity properties.
- Handle (‘dwg_handle’).
- Color (‘Color’).
- Entity type.
- Layer (‘Layer’).
- Layer Color.
- Line type (‘Linetype’).
- Line weight (‘Lineweight’).
- Hyperlink (‘Hyperlink’).
- Thickness (‘Thickness’).
- Blocks data: when checked, the data table will include new fields for the corresponding data of the Block References (if any).
- Name and Attributes (‘BlkName’) (‘Attribute Names’).
- Rotation (‘BlkRotation’).
- Scales (‘BlkXscale’, ‘BlkYscale’, ‘BlkZscale’).
- Texts data: when checked, the data table will include new fields for the corresponding data of the Text entities (if any).
- Contents (‘TxtString’).
- Rotation (‘TxtRotation’).
- Height (‘TxtHeight’).
- Hatches pattern data: when checked, the data table will include new fields for the corresponding data of the Hatch entities (if any).
- Name (‘HPatName’).
- Angle (‘HPatAngle’).
- Scale (Spacing for User patterns) (‘HPatScale’).
- Double (User patterns) (‘HPatDouble’).
- Geometry.
- Elevation: when checked, the data table will include a new field (‘Elevation’) whose value will be the elevation of the entities.
- Note: Regardless of this option, the application will use the entity elevation as Z-coordinate when exporting any XY-only entity (Circles, Polylines, etc.).
- Point coordinates: when checked, the data table will include new fields for the corresponding X/Y/Z coordinate values of the point-type entities (if any).
- X.
- Y.
- Z.
- Note: If the coordinates are transformed along the exporting process see this section, the transformed values will be exported instead of the original values.
- Length: when checked, the data table will include a new field (‘Length’) whose value will be the length of the entities.
- Area: when checked, the data table will include a new field (‘Area’) whose value will be the area of the entities.
- Elevation: when checked, the data table will include a new field (‘Elevation’) whose value will be the elevation of the entities.
- Other.
- Treat closed polylines as polygons: when checked (default value), all closed polylines in the drawing will be exported to the target as polygon features. Most of the time, the closed polylines represent polygonal elements in the target data format and this conversion can be automatic.
- Note: Be aware that, in order to avoid forgetting entities, in this case and in any other case where polygonal entities are exported to a polyline-type target, the polygon contours will be exported as polylines.
- Also export fields with null values.
- If not checked (default value): when you export to a target table with uniform fields structure (such as Shapefiles SHP), the table will include any field that has a non-null value in at least one entity of the export selection. When you export to a target table with non-uniform fields structure (such as KML), each entity will only include the fields that have a non-null value for the entity itself.
- If checked: in all cases, each entity and thus the entire table will include all the fields (null or non-null).
- Treat closed polylines as polygons: when checked (default value), all closed polylines in the drawing will be exported to the target as polygon features. Most of the time, the closed polylines represent polygonal elements in the target data format and this conversion can be automatic.
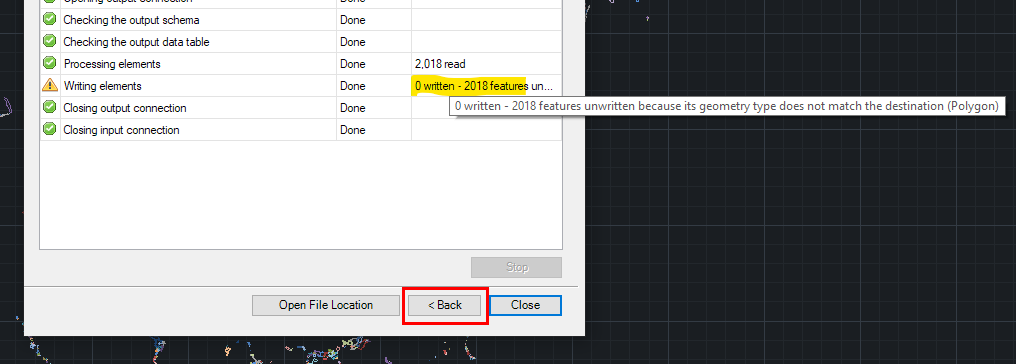
- Entities report: the application shows here the total number of the entities that will be exported and any warnings prior to the export process, such as the total number of unsupported entities that will not be exported or others.
When will duplicate fields be automatically renamed (by adding a correlative suffix) in the exported tables?
- When there are fields that can be found in different tables having the same name but different type. Those that can be found in different tables but have the same name and the same type are considered a single field.
- When a field (for example, “X”) already exists for any entity and the export options force adding a field with the same name (such as the “X” coordinate of the points).
“Back” button: As in the other application wizards, you will find the “Back” button in each step of the wizards in order to modify or add any previously introduced parameter. In the case of the “Export” wizard, this button is present even in the last step of the wizard and is applicable even after the export process is finished. Thus, if you detect that the export has failed or been incomplete due to some erroneous or partial parameter, you can comfortably repeat the process by modifying the wrong parameter(s) without having to modify any other.
- Tip: This tool can be an interesting time saver when you are exporting several types of entities to some target that only supports one particular type of entity. For example, assume you want to export all the entities in the drawing (linear, polygonal, points) to Shapefiles. You can select to export “All entities,” but when you define the type of feature that the Shapefile will contain you can only choose one type, since this is a limitation of Shapefiles. The application will filter the entities that can be exported to the chosen Shapefile type. But once the export is finished, the “Back” button will allow you to choose another type of feature for the target Shapefile without modifying any other settings (entity parameters, coordinate transformation, etc.) to quickly export the new type entities to another Shapefile.
- Note: The “Automatic” option that can be found when exporting to Shapefiles also simplifies this task because the export process will automatically create a different Shapefile for each entity type (Point, Polyline, etc.).
Configure the spatial target when exporting from BricsCAD
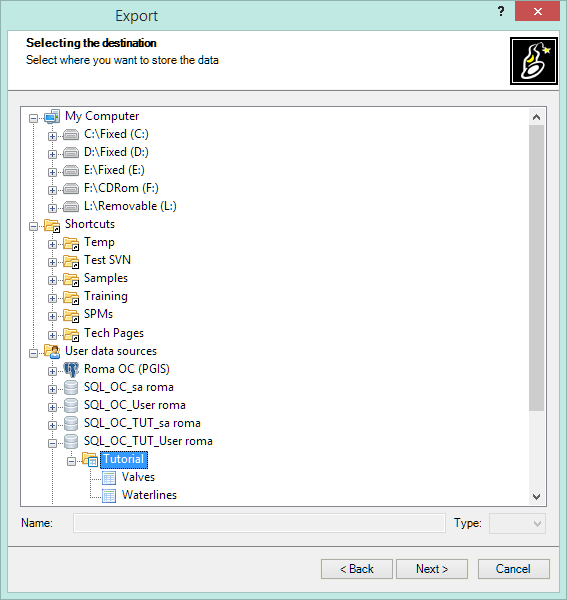
When you export using Spatial Manager™ for BricsCAD you must select the exporting destination. If needed, you also must select the data provider and its parameters.
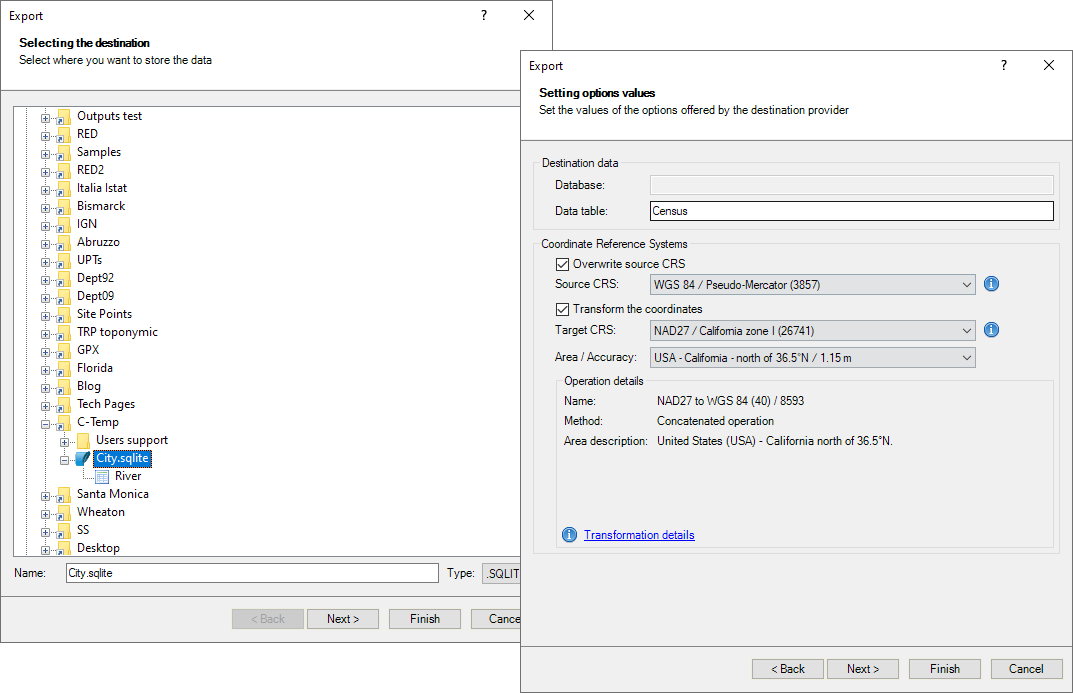
First, you select the destination for the exported data: a file or a table inside a file or a database (or inside a schema of a file or a database).
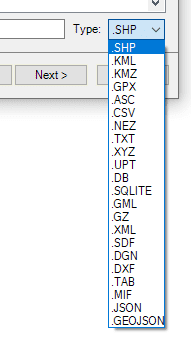
Next, you select a file type (the data provider). This step is not required if you have selected a UDS-based destination which defines its own data provider and provider parameters (such as a SQLite table, PostGIS table, a UDS for a simple file, etc.).
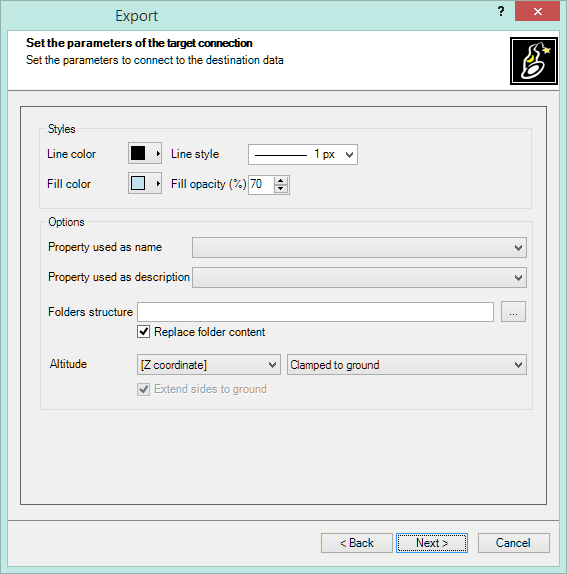
Then, you configure the export data provider connection parameters, if needed (Image: sample of the KML/KMZ files data provider).
Note: Although the application main palette (see Data sources) is the primary tool to manage resources and accesses, create/edit Shortcuts and User Data Sources (UDS), and other related functions, the context menus (right-click) in this Export window will also allow you to execute many of these functions “on the fly,” without having to return to the main palette.
Exporting geo-referenced images: Although the general Export functions allow exporting raster files in addition to vector files, the command SPMEXPORTIMAGE in Spatial Manager™ for BricsCAD is more straightforward for exporting geo-referenced images and, if needed, related geo-referencing additional files (Geo-reference and Coordinate System files).
Exporting additional geo-reference files of an image: In addition, although when exporting images it is possible to include additional geo-reference files (World, PRJ, etc.) in the export process, it is also possible to export only these additional files when the image is already stored as a separate file. This operation can be carried out using the command SPMWORLDFILE of Spatial Manager™ for BricsCAD.
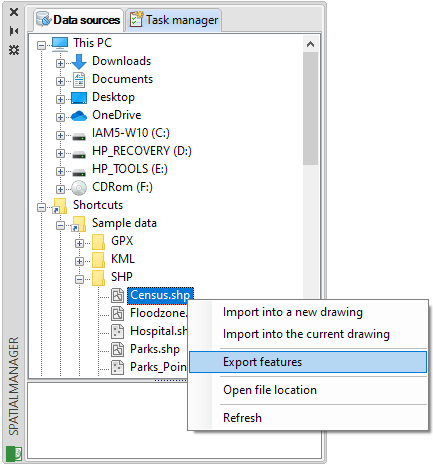
Export directly from a data source to another without importing into BricsCAD
You can directly export or convert from a data source to any supported data target by using the data sources contextual menu (right-click) in the main Spatial Manager™ for BricsCAD palette. This functionality allows you to run export processes without having to previously import the elements from the source data table into an BricsCAD drawing, and you will find similar options (coordinate system transformation, etc.) to those you can find when exporting BricsCAD entities.
Disclaimer:
- Some components shown here (providers, names, window styles, etc.) may differ slightly from those on your computer.
- Certain features require Internet access. If you experience issues, check with your network administrator about a possible Proxy server. You can configure the Proxy settings in the application options.
- Some geographic data providers (Geocode, image maps, etc.) may require a user account, which you can set up in the Service Provider API Keys section of the application options.